Concept of Resilience
Written on April 20th, 2020 by Chaewon Emily Park
Nowadays, I’m immersed in the concept of resilience. Resilience [in Korean, “회복탄력성”] is similar to elasticity- like you throw a rubber ball to the floor and it will bounce back. How ‘bout a glass jar? It’ll shatter the moment it crashes to the floor. Resilience has been considered an important business acumen- you might fail something, but as long as you have resilience to overcome that failure and spring up back on your feet, you will have come out even stronger, wiser, and experienced.
I feel like even the recent ongoing COVID-19 epidemic is a test to humanities’ (and specifically each country/government administration’s) resilience on medical system and government policies.
That got me thinking, when resilience is so important to humans,
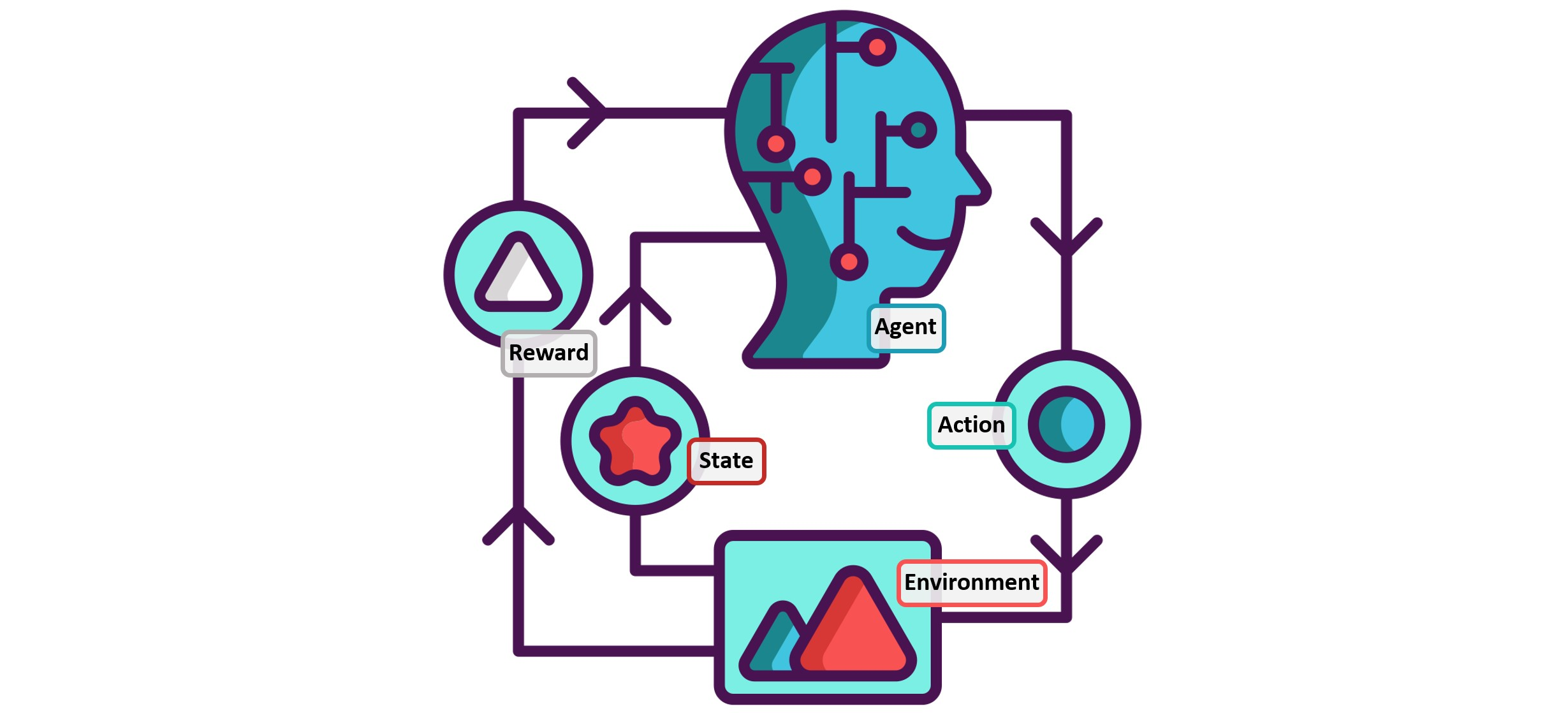
- What research efforts & discussions are being made to assess and develop resilience in AI?
- What kind of impact does lack of resilience have on current technology usage?
Resilience
- Ability for the system to acknowledge mistakes and adapt, mitigate, and overcome the situation by minimizing damage
- understand what is wrong
- figure out solution to overcome problem
- retain lessons learned and build upon it
- constant learning is needed for making a system that can evolve, adapt, and introspect
- 3 factors will help embed autonomy & self-perpetuated improvement that helps drive the system to think for itself
- a system that directs its own autonomy is important because humans CANNOT cover and consider all cases
- 3 factors will help embed autonomy & self-perpetuated improvement that helps drive the system to think for itself
The end goal is to guarantee a “measureable & repeatable level of confidence” in the resilience of a system by identifying, defining, and understanding policies, procedures, and practices
- Factors that makes resilience difficult
- Lack of sound data (Biased data, very little data, etc)
- Tricky Relationships (Wrong associative mapping between variables, nuanced relationships that are even difficult for humans)
Current Status of Research on Resilience
- Examples of compromised resilience
- Intended: Purposefully corrupting training data, Using mask/noise to gain unauthorized access, Creating deepfakes
- Unintended: Misjudgements by autonomous cars, wrong medical predictions/recommendations/diagnosis, system with racial & gender bias due to natural training data composition
-
Ensuring resilience & identifying vulnerabilities requires measuring resilience
- Current resilience assessment tools
- CERT-RMM (CERT Resilience Management Model)
- transparent human driven dialogue about risk is required to drive policies, procedures, and practices
- However, traditional resilience assessment tools are difficult to be applied on AI because
most ML models are a black box & datasets are getting massive
- Traditional: Simply interview people involved in the decision making process
-
Now: A black box model makes the decision… who are we supposed to interview?! Thus, we need information on the people who interact with the black box model and comprehensively try to understand how the model works in various scenarios
- <Questions to ask> - What is the ML system's expected baseline behavior? - How do we ensure the model has been trained properly? - How should we assess whether the model is making decisions (during testing time) that are coherent with the resilience policies? - How should updates on resilience policies and processes be reflected & propagated to ML systems? - When the ML model finds a method to improve resilience, how should it be communicated to the organization and be tracked? - How should feedbacks on bad results be provided and reflected on ML model? - How should scenario testing be designed to make model robust to rare circumstances? - Are there safety measures that prevents the ML model from deviating from safe training & testing procedures?
- CERT-RMM (CERT Resilience Management Model)
References: